Arabic letters with vowels—a fascinating system of diacritics and letters—are crucial for accurate pronunciation and understanding. This article delves into the intricate world of Arabic vowels, explaining their function, importance, and practical application. Without mastering these marks—known as harakat—you won’t just mispronounce words; you’ll potentially misunderstand entirely what a text is saying. This is because these subtle distinctions can change the meaning and even grammar of a sentence.
Understanding Short Vowels: The Harakat
Short vowels in Arabic, represented by diacritical marks, are often overlooked but are fundamental to comprehending the language’s nuances. These marks, placed above or below consonants, dictate the precise pronunciation of sounds, much like how accents in English can subtly shift the meaning of a word. Misinterpreting these marks can lead to significant misunderstandings, as a single vowel change can alter the entire meaning of a sentence.
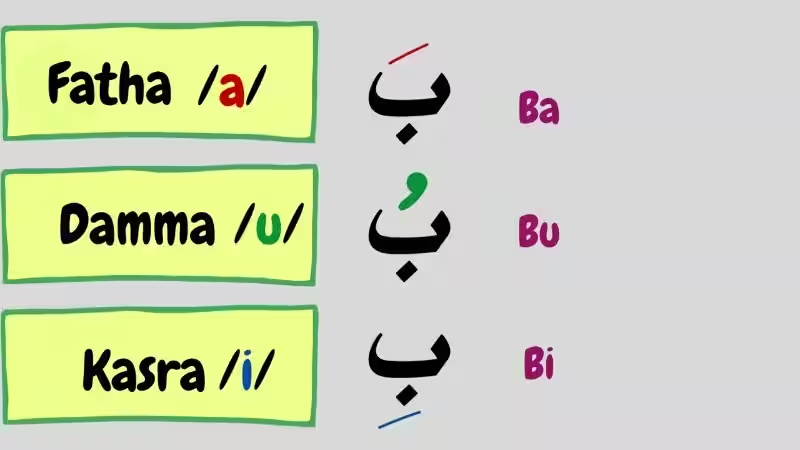
These harakat – Fathah (ـَ), Kasrah (ـِ), and Dammah (ـُ)—are not just decorative; they are vital indicators of short vowel sounds. Fathah corresponds to the “a” sound in “cat,” Kasrah to the “i” sound in “sit,” and Dammah to the “u” sound in “put.” These short vowels are often the difference between a word meaning “to write” and “to read,” for example. Their precise placement and combination with consonants are essential for fluent Arabic pronunciation.
The Significance of Omission
The omission of these short vowels can drastically alter the meaning of a word or even render it incomprehensible. Imagine trying to understand a sentence in English without any vowels. The same holds true in Arabic; without the harakat, the meaning becomes blurred or completely lost. This is why accurate use of these diacritical marks is so vital for clear communication.
Practical Application
To practice, try transcribing simple Arabic words and phrases, paying particular attention to the placement of these marks. You can find many online resources dedicated to Arabic pronunciation and vowel practice.
Deciphering Long Vowels: The Letters Themselves
Long vowels in Arabic are represented by distinct letters – Alif (ا), Waw (و), and Yaa (ي). These aren’t just consonants; they also convey vowel sounds of longer duration. This is similar to how different note lengths in music create different melodies; the length of the vowel sound determines the nuance of the word.
The long vowel Alif (ا) extends the “a” sound (as in “father”). Waw (و) extends the “oo” or “u” sound (as in “boot”). Lastly, Yaa (ي) extends the “ee” or “i” sound (as in “machine”). These letters themselves carry the extended vowel sound, as opposed to the short vowels’ diacritic markers.
The Dual Nature of Waw and Yaa
A crucial aspect of Arabic vowels is the dual nature of Waw (و) and Yaa (ي). They can act as both semivowels and long vowels. Consider the word “Howl” (حَوْلَ). Here, Waw acts as a consonant. In contrast, in “Hussein” (حُسَيْن), Waw is used to extend the long vowel sound. Understanding this duality is essential in discerning the linguistic context of the word.
Mastering the Rules
The rules governing the use of long vowels are important to grasp. For example, Alif must always be preceded by a Fathah to properly sound the long “ā” sound. Similarly, Waw and Yaa are associated with specific short vowel sounds when used to extend the long vowel. Comprehending these relationships is key to correct pronunciation and understanding.
The Grammatical Role of Vowels
Arabic vowels aren’t just about pronunciation; they play a critical role in grammar. The correct use of vowels often reveals the grammatical case (nominative, accusative, or genitive) of a noun, and its gender. This makes accuracy paramount.
For example, the word “He studied” (دَرَسَ) has a different vowel pattern than “Knowledge” (عِلْم) or “Box” (صُنْدُوق) or “Big” (كبير). These differences highlight the crucial role of vowels in determining grammatical structures. This distinction is not just about sound, it’s about conveying meaning within the linguistic framework.
Mastering Variation
The subtle variations in vowel use are essential for correctly communicating complex concepts and ideas. The difference between short and long vowels is not in the quality of the sound themselves but in the length of the sound. A short “a” differs in duration from a long “ā”. Understanding these distinctions is key to interpreting Arabic text accurately.
A Practical Guide to Arabic Vowels
Mastering Arabic vowels requires practice and consistent application. To aid you in this process, here’s a practical approach:
- Start with short vowels: Focus on recognizing and producing the sounds of Fathah, Kasrah, and Dammah first. Use online resources or language learning apps to practice these sounds with words.
- Progress to long vowels: Once you’re comfortable with short vowels, move on to the letters Alif, Waw, and Yaa. Practice pronouncing words with both short and long vowels.
- Learn the dual function of Waw and Yaa: Understand the distinction between Waw and Yaa as semivowels and long vowels in various contexts.
- Combine vowels with consonants: Practice combining letters and vowels to pronounce simple words and phrases.
- Seek feedback: Ask a native speaker for feedback on your pronunciation to identify areas for improvement.
By employing these strategies, you’ll discover that Arabic letters with vowels are not intimidating; rather, they are the key to unlocking the beauty and complexity of the Arabic language.
This journey into the world of Arabic vowels is just the beginning. By understanding these subtleties, you unlock not just the correct pronunciation but also the rich tapestry of meaning and grammatical precision of the language. Continuous practice and dedicated study will ensure you confidently navigate the world of written and spoken Arabic. Remember, mastering these intricacies is essential for accurate pronunciation, clear communication, and a deeper appreciation for the beauty of the Arabic language.
What are the Arabic vowels?
Arabic vowels, essential for accurate pronunciation and understanding, are a distinct system from English. They are called harakat (diacritical marks) and significantly affect word meaning and grammar. This system includes short vowels, represented by marks above or below consonants, and long vowels, represented by specific letters.
What are the short vowels, and how do they sound?
There are three short vowels:
- Fathah (َ): Pronounced like the “a” in “cat” or “father” (short a).
- Kasrah (ِ): Pronounced like the “i” in “sit” (short i).
- Dammah (ُ): Pronounced like the “u” in “put” (short u).
These marks are placed above or below the consonant letters. Omitting or misplacing these marks can completely change the meaning of a word.
What are the long vowels, and how do they sound?
There are three long vowels, represented by distinct letters:
- Alif (ا): Represents a long “a” sound, similar to the “a” in “father” (long a).
- Waw (و): Represents a long “oo” sound, similar to the “oo” in “boot” (long oo), or a consonant “w”.
- Yaa (ي): Represents a long “ee” sound, similar to the “ee” in “sheep” (long e), or a consonant “y”.
These letters themselves function as vowels. Alif is always preceded by a Fathah, and Waw and Yaa have specific vowel sounds associated with them.
What is Sukun (ْ)?
Sukūn (ْ) is a mark that indicates the absence of a vowel sound on a consonant letter. It signifies the end of a syllable.
What is the difference between short and long vowels?
The difference between short and long vowels is not in the quality of the sound but in its duration. Short vowels are brief, while long vowels are sustained. This is analogous to the difference between musical notes of different lengths.
How do Waw (و) and Yaa (ي) function as both vowels and consonants?
Waw (و) and Yaa (ي) can represent both long vowel sounds and consonant sounds depending on the context. For example, in the word “Howl” (حَوْلَ), Waw is a consonant, whereas in “Hussein” (حُسَيْن), it’s part of a long vowel sound. The same applies to Yaa.
Why are Arabic vowels important?
Arabic vowels are crucial for accurate pronunciation, clear communication, and understanding the nuances of the language. They also indicate the grammatical case and gender of nouns and adjectives. Misusing or omitting vowels can drastically alter the meaning of a word.