The Arabic Numerals: A Journey from East to West
Arabic numerals, the ones we use every day to represent numbers, have a fascinating history. While we often associate them with the Arabic world, their origin lies in the ancient Indian numeral system. The numerals we use today, known as Western Arabic numerals, were adopted from the Indian system and eventually spread to the West.
However, this isn’t the only system of Arabic numerals. The Eastern Arabic numerals, used in North Africa and parts of the Middle East, are a slightly different variant of the Indian system, adopted by Arabs. These numerals have a distinct visual appearance compared to the Western ones. For example, the number 0 in Eastern Arabic numerals appears as a small circle (٠), while in Western Arabic numerals, it appears as a more open oval (0).
Counting from Zero: A Glimpse into Arabic Numeration
In Arabic, the concept of zero is represented as صفر (sifr). It’s the starting point for counting, just as it is in other languages.
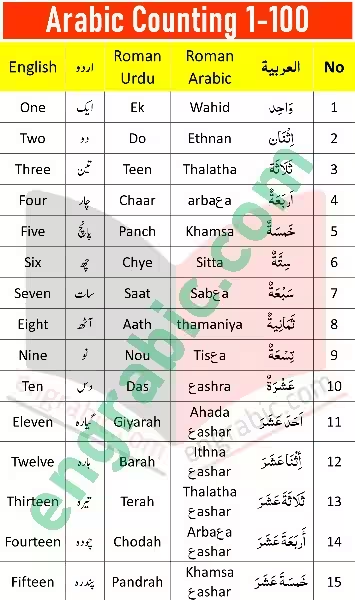
Let’s explore how Arabic counting works from 0 to 10, considering the differences in the Eastern and Western systems:
| Number | English | Western Arabic | Eastern Arabic | Arabic Word |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Zero | 0 | ٠ | صفر (sifr) |
| 1 | One | 1 | ١ | واحد (wāḥid) |
| 2 | Two | 2 | ٢ | اثنان (ithnān) |
| 3 | Three | 3 | ٣ | ثلاثة (thalātha) |
| 4 | Four | 4 | ٤ | أربعة (arbaʿah) |
| 5 | Five | 5 | ٥ | خمسة (khamsa) |
| 6 | Six | 6 | ٦ | ستة (sita) |
| 7 | Seven | 7 | ٧ | سبعة (sabʿah) |
| 8 | Eight | 8 | ٨ | ثمانية (thamāniyah) |
| 9 | Nine | 9 | ٩ | تسعة (tisʿah) |
| 10 | Ten | 10 | ١٠ | عشرة (ʿasharah) |
The Gender Game: A Unique Feature of Arabic Counting
One intriguing aspect of Arabic counting is the concept of gender agreement. This means that the number’s gender is determined by the opposite gender of the item being counted. This rule applies from 3 to 10.
For example, “four books” is أربعة كُتُب (arbaʿah kutub), where the number arbaʿah (four) is masculine, while “four magazines” is أربع مجلّات (arbaʿ majallāt), where the number arbaʿ is feminine. The gender of the noun “books” is feminine, so the number takes on the masculine form, and vice versa.
This gender agreement adds a layer of complexity to Arabic counting, but it also makes it a truly fascinating system to explore.
Beyond Ten: A Glimpse into Arabic Numeration
Counting in Arabic beyond ten follows a pattern that combines the numbers we’ve already seen.
For example, 11 is أحد عشر (aḥad ʿashar), literally “one and ten”. 12 is اثنا عشر (ithnā ʿashar), “two and ten.”
As you progress, the pattern becomes more apparent. 20 is عشرون (ʿishrūn), 30 is ثلاثون (thalāthūn), and so on.
Conclusion: The Power of Zero in Arabic
From the humble zero to the intricacies of gender agreement, Arabic numeration offers a fascinating glimpse into the language’s rich linguistic structure. Understanding how Arabic numbers work can open doors to a deeper appreciation of the language and its cultural significance.
As you delve deeper into Arabic, you’ll discover that numbers play a vital role in expressing time, dates, quantities, and more. This knowledge will not only enhance your understanding of the language but also enrich your experience with Arabic culture.
Frequently Asked Questions about 0 in Arabic
What is the Arabic word for zero?
صِفْر (ṣifr)
How do you write zero in Arabic numerals?
٠
- Arabic numerals are written from left to right, unlike Arabic letters.
- Arabic numbers are crucial for understanding modern standard Arabic.
- The table lists numbers from 0 to 19, including masculine and feminine forms.
- Numbers from 20 to 30 are also covered.
- Multiples of 10 up to 90 are included.
- Numbers 100 and 1000 are presented.
- Larger numbers like 2000, 100,000, and 1 million are included.
- The content provides a comprehensive guide to Arabic numerals, both cardinal and ordinal numbers.
- The Arabic words for both cardinal and ordinal numbers are included.
- The content emphasizes the importance of learning Arabic numbers for understanding the language.
- Arabic numbers are presented in both Arabic script and English transliterations.
- The resource is helpful for anyone who wants to learn to count in Arabic.
- The content provides a solid foundation for understanding Arabic numeration system.
- The resource serves as a starting point for learning Arabic numbers.
- The content includes useful links for further exploration.
- Arabic numbers are essential for understanding Arabic culture and society.
- The resource is valuable for students of Arabic language and culture.
- The content covers a range of numbers from 0 to 1 million.
- The table provides a clear and concise presentation of Arabic numbers.
- The resource can be used for both self-study and classroom instruction.
- The content is presented in an accessible and engaging manner.
- The resource provides a valuable tool for anyone interested in learning Arabic.
- The content is comprehensive and up-to-date.
- The resource is well-organized and easy to navigate.
- The information is presented in a logical and sequential order.
- The resource is a valuable addition to any Arabic language learning materials.
- The content is accurate and reliable.
- The resource is free and easily accessible.
- The content is relevant to a wide audience.
- The resource is a valuable asset for anyone interested in Arabic language and culture.