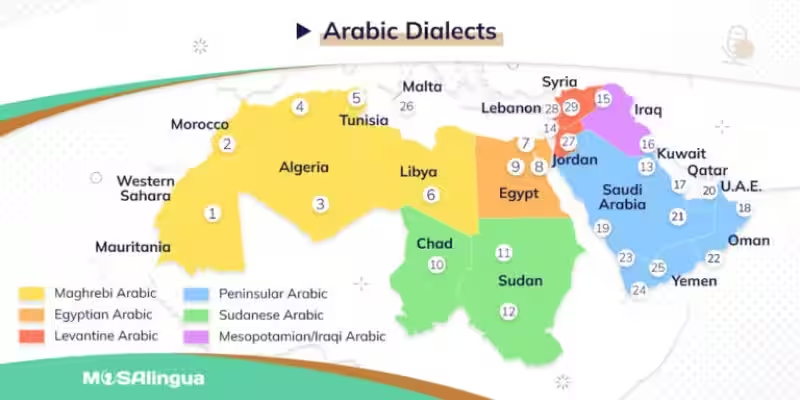
The question of learning an Arabic dialect, especially for someone already proficient in Standard Arabic, touches upon a crucial difference: the formal and colloquial. Standard Arabic (الفصحى) provides a unifying linguistic framework, but understanding its regional variations and the related dialects is essential for effective communication. Navigating this dialectal landscape is a complex undertaking, with each dialect possessing its unique structure, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Therefore, deciding which Arabic dialect should be learned is a significant question, especially for learners already familiar with Standard Arabic.
The Challenge of Dialectal Diversity
Learning an Arabic dialect for everyday communication, particularly for those fluent in Standard Arabic, reveals a significant complexity. Arabic dialects are far more than just variations; they often represent distinct languages with substantial differences in grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. This makes the idea of a single “most useful” dialect for cross-cultural understanding across the entire Arabic-speaking world virtually impossible to achieve. There’s no universal key; each region maintains its own unique communication style. This inherent diversity drastically impacts the learner’s path, demanding careful consideration.
Beyond the “One-Size-Fits-All” Dialect
Instead of searching for a dialect that guarantees universal understanding, a more strategic approach is key. The goal is not just to find the easiest dialect, but to identify the one that best aligns with the learner’s communicative needs and the specific region where they plan to interact. Consider these factors:
- Geographical Location: Dialects prevalent in a specific region will be more useful for interaction in that area.
- Intended Activities: Will the learner engage with local communities, attend religious services, or participate in cultural events? The dialect used in those activities will be the most beneficial.
- Target Audience: Is the goal to communicate with specific groups or individuals? This will significantly impact the choice of dialect.
This approach prioritizes effective communication within a particular context, rather than aiming for universal fluency.
Understanding Linguistic Relationships
Understanding the linguistic relationships between dialects can be invaluable. Some dialects share more cognates and grammatical similarities than others. This knowledge can accelerate the learning process by recognizing underlying structural similarities. However, it’s crucial to avoid the misconception that this understanding guarantees easy transition between all dialects. While recognizing shared roots can be helpful, the differences within dialects are substantial.
Navigating the Complexity of Linguistic Structures
Recognizing that Arabic dialects aren’t simply variations but often distinct languages is crucial. Understanding the historical and geographical connections between dialects can reveal patterns and shared features. For example, dialects spoken in neighbouring regions may share more similarities than dialects separated by vast distances. This knowledge, however, does not ensure effortless transition between dialects. Careful study and dedicated effort are still paramount. Ultimately, a solid understanding of the nuances of a particular dialect is required for effective communication.
Sociolinguistic Context and Personal Factors
The sociolinguistic context is equally important. While a dialect might be geographically widespread, its use might be limited to particular social groups or regions. A widely understood dialect might not be ideal for a specific niche communication need.
Beyond the Linguistic Structure
The learner’s personal learning style, previous language learning experiences, and the availability of resources and teachers also play a pivotal role. Ease of access to learning materials, online resources, and the availability of native speakers can significantly impact the learning journey. A dialect with abundant online resources or a strong community of speakers can streamline the learning process.
A Strategic Learning Approach
Instead of focusing on one “easiest” dialect, a more strategic approach involves gaining a strong grasp of the linguistic characteristics of a few closely related dialects in a particular region. Understanding the linguistic landscape within a region offers a more comprehensive understanding of the language’s nuances.
Tailoring the Learning Path
Learning a dialect with a wealth of literature and linguistic analysis can provide valuable insights into the broader linguistic landscape. Alternatively, focusing on a dialect spoken in a region with a high concentration of native speakers offers more opportunities for practice and refinement. Ultimately, the learner should select the dialect that most effectively supports their communication goals.
Conclusion: A Realistic Approach to Arabic Dialects
Effective communication in Arabic requires a realistic understanding of the complexity of Arabic dialects. It necessitates a proactive approach to learning, adaptability, and a willingness to embrace the nuances of each dialect. The focus should be on developing strong communication skills within a particular region or context, rather than pursuing comprehensive linguistic fluency in all dialects. Recognizing that mastering multiple dialects might require significant time and dedication is essential. The learner should prioritize their communication needs, considering their target audience and the intended use of the dialect. This proactive and adaptable approach ensures a meaningful and successful learning experience.
FAQ: Which Arabic Dialect Should I Learn?
This FAQ addresses the complexities of choosing an Arabic dialect to learn, particularly for those already proficient in Standard Arabic.
What is the best Arabic dialect to learn?
There’s no single “best” dialect. Arabic dialects are highly diverse, often representing distinct languages rather than variations. No single dialect guarantees understanding across the entire Arabic-speaking world. Instead of focusing on a universally understood dialect, consider your specific communication needs and the region you intend to interact with.
I already know Standard Arabic (الفصحى). How will learning a dialect affect my understanding?
Standard Arabic provides the grammatical and vocabulary foundation. However, dialects often feature different grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. Learning a dialect will allow you to bridge the gap between formal and colloquial language, enabling more natural and effective communication.
How diverse are Arabic dialects?
Arabic dialects vary significantly, not just in pronunciation and vocabulary, but also in grammar and syntax. Some dialects are more closely related, sharing more cognates and grammatical similarities. However, this shared lineage doesn’t guarantee effortless transition between all dialects.
Can I learn multiple dialects?
While possible, mastering multiple dialects requires significant time and effort. It’s more practical to focus on one or a few dialects that align with your communication needs and regional interests.
What factors should I consider when choosing a dialect?
Several factors influence the best dialect choice:
- Communication needs: Do you need to understand and be understood in a specific region or community?
- Geographical proximity: Choose a dialect spoken in a region where you intend to travel or interact frequently.
- Cultural immersion: Do you want to engage with movies, music, or other cultural expressions?
- Learning resources: Look for dialects supported by ample online resources, language learning materials, and teachers.
- Personal learning style: Select a dialect that aligns with your preferred learning methods, resources, and community support.
What are some examples of dialects often recommended?
While a definitive “best” dialect doesn’t exist, some frequently recommended dialects include:
- Egyptian Colloquial Arabic: Widely understood across many Arabic-speaking countries, prevalent in Arabic media, and suitable for everyday communication.
- Modern Standard Arabic (MSA): The official language of many Arab countries, used for formal communication, and useful for those interested in Quranic studies or Islamic texts.
What if I don’t know where to start?
Start by researching the dialect spoken in a region you are interested in. Focus on learning a few closely related dialects within a specific region to observe the underlying linguistic structures. This will also be helpful for the learner to gradually transition to different dialects if needed. Learning a dialect with a rich literary tradition or one with significant online resources can enhance your comprehension of the larger linguistic landscape of Arabic dialects. Remember that learning any dialect is a journey that requires patience, dedication, and adaptability to the nuances of each dialect.